| IN A NUTSHELL |
|
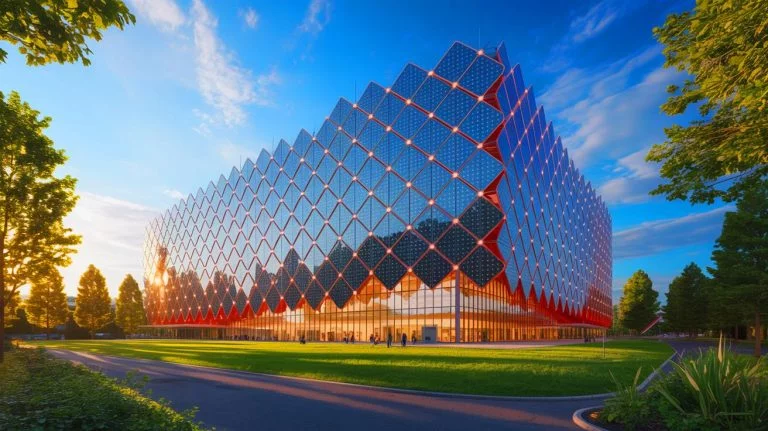
In the picturesque city of Basel, Switzerland, a groundbreaking architectural marvel is redefining sustainable energy use. The Novartis Pavilion stands as a testament to innovative design and eco-friendly technology, capturing global attention with its unique ability to harness both solar and wind energy. This cutting-edge structure, enveloped in a living skin of 10,000 diamond-shaped solar modules and 30,000 LEDs, not only powers itself but also showcases a spectacular fusion of art and science. As cities worldwide grapple with energy challenges, the Novartis Pavilion offers a visionary glimpse into the future of sustainable architecture.
The Novartis Pavilion Wrapped in Skin
The Novartis Pavilion is an architectural wonder that blurs the line between a building and a living organism. Designed by the Italian studio AMDL Circle in collaboration with Swiss media architecture firm iart, its media façade acts like biological skin, breathing life into the structure. The 10,000 solar cells enveloping the pavilion are not your typical solar panels. They are lightweight and draw inspiration from the natural world, mimicking the very cells and molecules that surround them. This innovative design is a testament to the fusion of technology and nature.
During the day, these solar cells diligently capture the sun’s energy, while at night, the pavilion transforms into a canvas projecting art and scientific imagery developed in collaboration with Novartis researchers. The result is not just a building, but a vibrant work of art that engages and inspires all who visit. This transformative use of technology and design underscores the potential of architecture to go beyond functionality, creating spaces that are both energy-efficient and aesthetically remarkable.
Switzerland’s Solar and Wind Power Agenda
The Novartis Pavilion is a cornerstone of Switzerland’s ambitious agenda to integrate solar and wind power. Its design is meticulously crafted to maximize energy efficiency by harnessing both solar and wind energy. The structure’s steel frames facilitate enhanced air circulation, boosting the overall energy output. This dual-energy approach has resulted in a record-breaking power surge, surpassing the building’s total energy consumption—a remarkable achievement that sets a new standard for energy-neutral buildings.
Engineers behind this innovative project have achieved what many thought impossible: a building that generates all the energy it requires. The pavilion’s self-sufficiency in powering its lighting and interactive media systems is a testament to the power of integrating renewable energy sources. This achievement represents a significant step towards a future where buildings are not just consumers of energy, but active producers, contributing to a more sustainable urban environment.
Sustainability at the Forefront
The Novartis Pavilion is more than an energy-generating powerhouse; it is a symbol of sustainability and artistic expression. Its design captures the essence of innovation, transforming solar panels into a dynamic work of art after sunset. Artists like Daniel Canogar and Esther Hunziker have contributed to this transformation, creating visual narratives that reflect the core values of sustainability and scientific exploration. The pavilion’s “Wonders of Medicine” installation offers visitors an insightful journey through the past, present, and future of healthcare, underscoring the pavilion’s role as an educational and inspirational space.
This remarkable fusion of art and science is not just a spectacle; it is a call to action, urging societies to embrace the possibilities of renewable energy. The Novartis Pavilion stands as a beacon of hope, demonstrating that sustainable design can be both beautiful and functional. It challenges us to rethink our approach to architecture and energy, inviting us to imagine a future where buildings are not only energy-neutral but also sources of inspiration and learning.
Ensuring an Energy-Brighter Future
The Novartis Pavilion, with its 10,000 solar modules and record-breaking energy generation, offers a glimpse into a future where design and energy converge seamlessly. This bold, futuristic structure is not just a marvel of engineering but also a symbol of hope for cities worldwide moving towards energy-neutral buildings. By integrating storytelling and energy generation, the pavilion highlights the potential of architecture to address global energy challenges creatively and effectively.
As the world grapples with the effects of climate change, the Novartis Pavilion serves as a model for what is possible when innovation and sustainability go hand in hand. Its design elements intertwine to create a structure that is not only functional but also visually captivating. The pavilion’s ability to generate power and communicate a message of sustainability is a powerful reminder of the role architecture can play in shaping a greener future. As we look towards this future, the question remains: How can we continue to innovate and reimagine our built environment to better serve the planet?
Did you like it? 4.4/5 (23)




Wow, the Novartis Pavilion sounds incredible! How does it compare to other sustainable buildings out there? 🌿
Are there any plans to replicate this kind of architecture in other countries? The world needs more of this! 🌎
It’s amazing what can be achieved with renewable energy. But are the costs of building such a pavilion sustainable in the long run?
Just when you thought buildings couldn’t get cooler, they start acting like living organisms. Mind blown! 🤯
Does anyone know how they manage the maintenance of all those solar modules and LEDs?
Great to see innovation in green energy! But I wonder about the energy payback time for such structures. 🤔
I’m curious, how do they balance art and utility in such a complex design?
It’s a fantastic concept, but how much does it cost to build a pavilion like this?
Thanks for the article! Really makes you think about the future of architecture. 😊
Is it really practical to integrate such technology in densely populated urban areas?
Wow, I didn’t realize buildings could be so artistic and functional at the same time!
Does the pavilion have any educational programs for visitors? 🎓
Why isn’t this kind of project more common? Seems like a no-brainer for sustainable development.
Are there any drawbacks to using solar and wind energy together like this? 🔋
Incredible! But how does it perform during overcast days or in winter? ☁️
This is the future of architecture! But do we have the technology to scale this up globally?
It’s fascinating, but could the energy surplus be used for other purposes?
Can we expect to see similar projects in cities like New York or Tokyo anytime soon? 🏙️
What sort of impact does this have on the local community in Basel?
Impressive! But are there any environmental downsides to this technology?
How do they ensure the art installations remain fresh and engaging over time? 🎨
This sounds like a rich man’s playground. Is it really accessible to the general public? 🤔
Would love to see something like this in my city. Who do I talk to about making it happen?
Is the building open to tourists? Seems like a great place to visit and learn!
Can older buildings be retrofitted with this kind of technology, or is it only for new constructions?
Who are the key collaborators behind this project? Seems like a massive team effort. 👥
Are there any plans for similar projects in developing countries where they are needed most?
Seems like a great step forward, but how do we address the energy needs of less sunny regions?
Innovative indeed! But how much of this is hype versus real, practical application?
Can’t wait to see how this influences future construction projects worldwide! 🏗️
Why do these projects always seem to be in wealthy countries? 🌍
This is just the beginning, right? What other futuristic projects are in the pipeline?
It’s cool, but I wonder how long it takes before such a building becomes energy-neutral?
What kind of scientific storytelling does the pavilion engage in? Sounds intriguing! 📖
How do they manage the transition from day to night with all those lights and displays?
Amazing article! I’ll be sharing this with my friends who are interested in renewable energy. 👍