| IN A NUTSHELL |
|
The medical technology landscape is witnessing a groundbreaking shift, courtesy of a South Korean research team. Their innovative approach to recharging implantable medical devices without surgery is set to revolutionize patient care. As the prevalence of conditions necessitating these devices increases, so do concerns about their long-term sustainability and safety. The traditional method of replacing exhausted batteries through surgery poses significant risks and discomfort to patients. This new ultrasound-based wireless charging solution promises to alleviate these concerns, offering a safer and more efficient alternative that could redefine patient care standards.
Revolutionizing Medical Device Charging
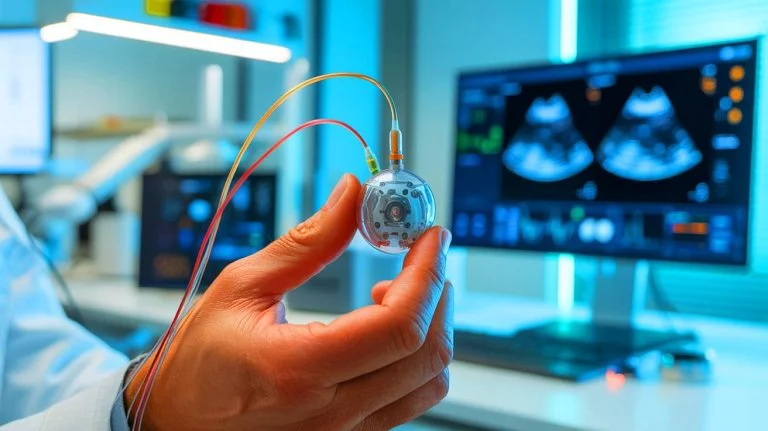
The innovative system developed by Professor Jinho Chang and his team at the Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) leverages dual piezoelectric layers to convert ultrasound waves into electricity. This novel approach allows the system to safely recharge implantable device batteries without the need for surgical intervention. The first layer captures incoming ultrasound waves, while the second layer harnesses residual energy, effectively doubling the power output compared to conventional methods.
By optimizing the design through simulations, the researchers achieved a power density of 497.47 milliwatts per square centimeter in water. This translates to fully charging a 140mAh battery in just 1.7 hours. Such efficiency marks a significant advancement in the field, addressing a long-standing challenge in the management of implantable medical devices. The potential to decrease the frequency of surgical interventions cannot be overstated, offering a beacon of hope for patients worldwide.
Testing the Technology’s Limits
To ensure the technology’s real-world applicability, the research team conducted tests using pig tissue to simulate human anatomical conditions. Even with a 30mm-thick tissue layer, the harvester managed to deliver 312.34 milliwatts of power, demonstrating its robust performance. These experiments underline the technology’s ability to function efficiently under realistic conditions, a critical factor for its eventual adoption in medical settings.
Professor Chang highlighted the technology’s potential, stating, “This research presents an innovative technology that effectively harvests ultrasound energy, which has not been fully utilized in the past, for wireless charging of implantable medical devices.” Such advancements pave the way for reduced surgical interventions and could lead to the development of smaller, more efficient electronic implants.
Implications for the Future
The implications of this breakthrough extend far beyond technical innovation. If successfully commercialized, this technology could eliminate the need for repeated surgeries, significantly enhancing patient quality of life. The prospect of smaller, smarter, and longer-lasting medical devices aligns with broader trends toward miniaturization and increased functionality in medical technology.
Moreover, the system’s potential to charge devices within an hour could redefine emergency care protocols and chronic condition management. With continued research and development, this approach may soon become a standard practice in medical device manufacturing and patient care, offering a new lease on life for millions of patients globally.
The Road to Commercialization
While the research is still in its nascent stages, the team’s ambitions are clear. They aim to refine the technology further by integrating high-efficiency semiconductor components, striving for a commercially viable system capable of rapid charging. The study, published in the journal Biosensors and Bioelectronics, has already garnered significant attention, signaling the beginning of what could be a transformative era in medical device technology.
As global populations continue to age, and the prevalence of chronic conditions rises, the demand for reliable and efficient medical technologies will only increase. The successful commercialization of this ultrasound-based charging system could catalyze further innovations in the field, challenging researchers and industry leaders to rethink the possibilities of implantable medical devices.
The development of this ultrasound-based charging system for implantable devices marks a pivotal moment in medical technology. As researchers work towards commercialization, questions remain about the broader impact on healthcare systems globally. How will this innovation shape the future of patient care and medical device development?
Did you like it? 4.6/5 (21)




Wow, this sounds like a game-changer for patients with pacemakers! 😊
Can this technology be applied to other medical devices as well?
How long before this becomes widely available? I have a family member who could really benefit from it.
So, no more scars from surgeries? That’s incredible!
I’m a bit skeptical. How safe is this ultrasound technology for long-term use?
Thank you to the researchers for making life easier for so many patients! 🙌
This sounds too good to be true. What’s the catch?
Does this mean fewer hospital visits for pacemaker patients? I’m all for it!
Can this technology withstand the test of time or will it need frequent upgrades?